The advantages of laser drilling
Laser drilling is a force- and contact-free machining process. Therefore, there is no deformation of the material by tools. Furthermore, there are no additional tooling costs by wear.
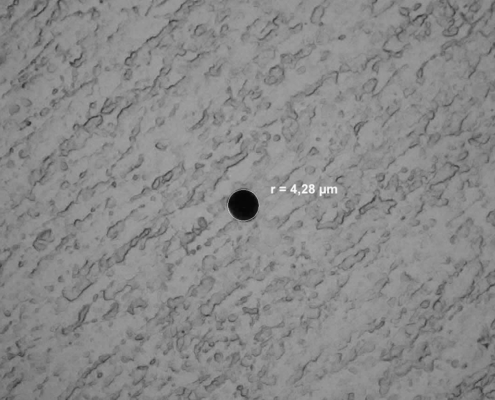
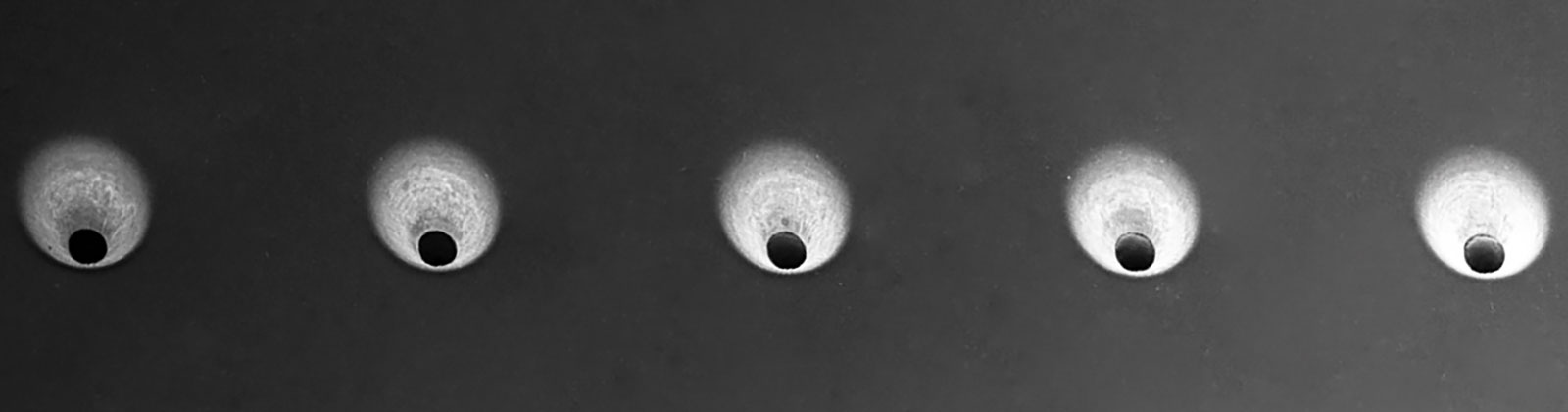
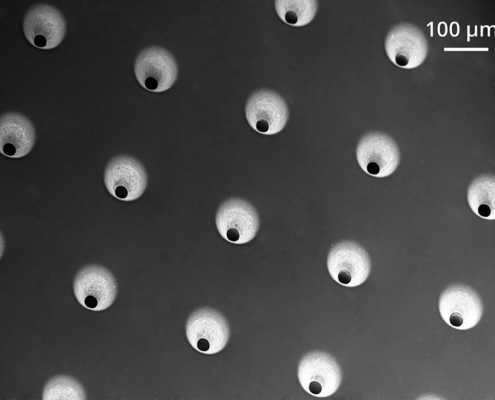
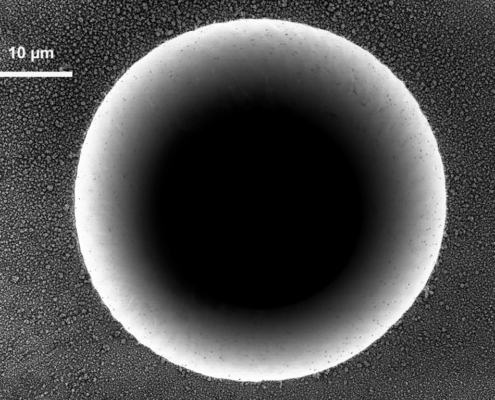
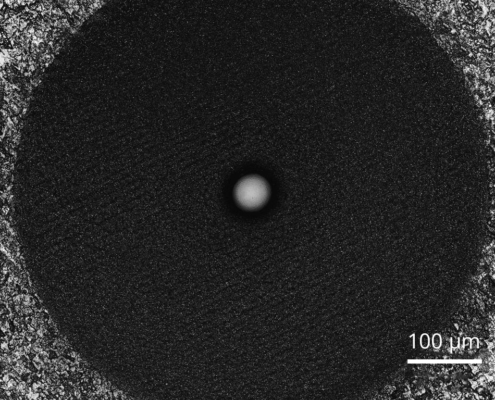
Laser technology convinces with its precisely dosed energy input, the low heat input into the material, and the extraordinarily high precision and reproducibility. Postprocessing is not necessary.
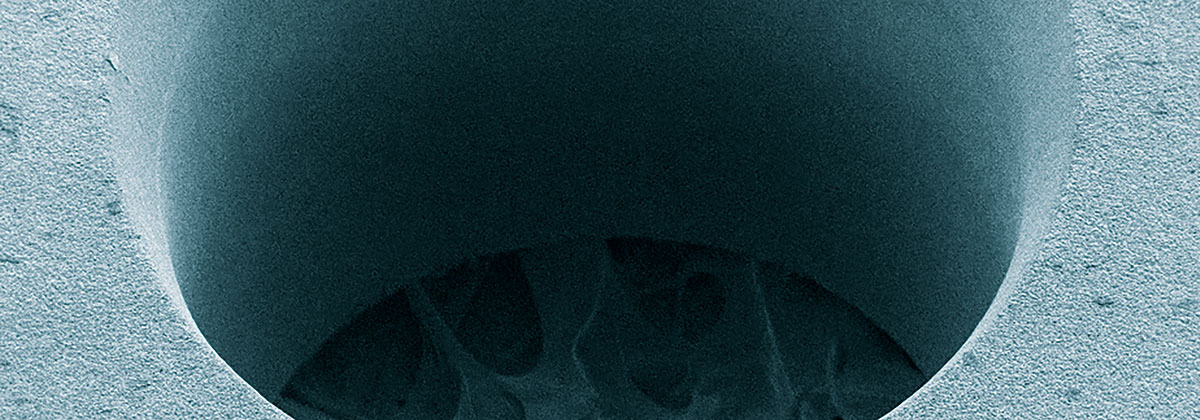
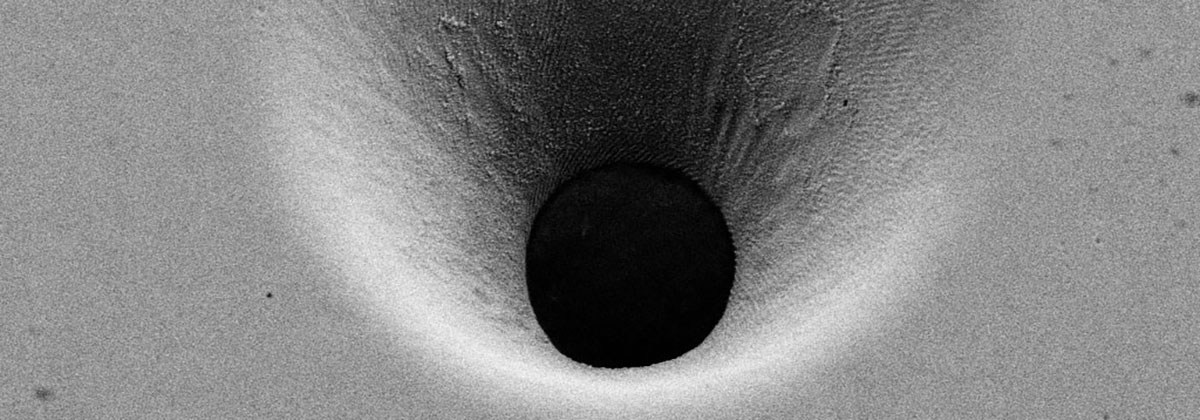
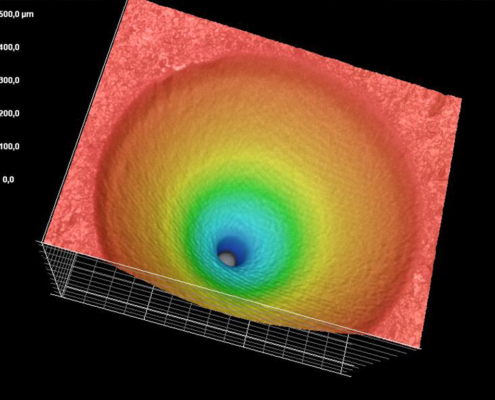
Additional advantages appear from the flexibility in the bore geometry. For example, it is possible to produce micro-holes with a large aspect ratio (the ratio of drilling depth to hole diameter) or even holes with defined wall angles by varying the machining strategy.
Areas of application
- Medical technology
- Electronics
- Automotive industry
- Semiconductor industry
- Metals (stainless steel, brass, Al, Au, Ag, Ni, Wo, etc.)
- Ceramics (Al2O3, ZrO2, PZT…)
- Glass (B33, Nexterion, Quartz glass, Sapphire, High Index…)
- Polymers (stacks, PET, PI, stacks with metal layer…)
- Semiconductors (Si, SiC)
- Thin films (ITO, MAM…)
Laser sources
Depending on the application and task, different lasers are used to produce micro-holes. While excimer or solid-state lasers in the UV range are often used for plastics, solid-state lasers in the visible or infrared spectral range are mainly used for metal processing.
The size of the holes depends, among other things, on the material, beam source, pulse duration, and energy density. Therefore it can vary from a few micrometers to several millimeters. Another decisive factor is the choice of a drilling technique.